Thermodynamics - Use of boilers in today's Industries
Boilers
Introduction:
A boiler can be said as an enclosed pressure vessel which with help of combustion of fuel is used for converting water into steam. Quick fact “Volume of water increases 1600 times when converted into steam”.
Image credit:www.indiamart.com
One of the most important boilers is in the power generation industry. For a generation of power, the steam generated in the boiler is used to turn the turbine which in return converts mechanical energy into steam energy. Most conventional steam boilers are classed as either fire-tube or water tube types. In the fire-tube type, the water surrounds the steel tubes through which hot gases from the furnace flow. The steam generated collects above the water level in a cylindrically shaped drum. A safety valve is set to allow the escape of steam at pressures above normal operating pressure; this device is necessary on all boilers because continued addition of heat to water in a closed vessel without means of steam escape results in a rise in pressure and, ultimately, in an explosion of the boiler. Fire-tube boilers have the advantage of being easy to install and operate. They are widely used in small installations to heat buildings and to provide power for factory processes. Fire-tube boilers are also used in steam locomotives.
Most of the Boiler basically works on the Rankine cycle.
image credit:www.wikipedia.com
Rankine cycle is a modification done to the Carnot cycle thereby removing its inefficient component and achieving practically closer results.
Types of Boiler and Classifications of Boiler:
There are the following Boilers Types:
1. According to the position of water and hot gasses
- Fire-tube boilers.
- Water-tube boilers.
2. According to Axis of Shell
- Horizontal Boilers.
- Vertical Boiler. References:www.britanica.com
FIRE TUBE BOILER
The Fire tube boiler is intended for transmitting hot-gases using heat source as well as cycle. These gases flow through pipes with a water-filled drum. This procedure efficiently transmits the heat from the hot gas to the water, which efficiently produces steam. The main features of fire tube boilers include a simple design, easy to operate as well as low cost to purchase. These boilers are extremely flexible in producing the average to low degrees of force with the capacity as well as skilled to be arranged in different designs.
What is Fire Tube Boiler?
These are one of the most fundamental and old designed boilers. These boilers are very famous in the 18th century, and especially applicable for train engines. In this kind of boiler, combustion of heat, as well as gases, flows through the pipe enclosed by water. These boilers may be high-pressure or low-pressure boilers. The measurement of these boilers can be done always with their external diameter. Generally, these boilers are intended for pressures up toward a highest of 250 psi & around 750 horsepower.
Construction and Working Principle of Fire Tube Boiler
The construction of a water tube boiler can be equipped with cylindrical shell, vertical, the firebox in the base, space for water in the center segment, and space for steam in the higher segment. A fire-grate is located at the fire-box base as well as coal is fired-up on the firebox. For burnt coal, an ash pit is placed at the base of the grate for gathering the ash from the burnt coal, and sometimes it can be detached.
One of many cross-tubes are flanged to the space of water that is placed within the box to raise the outside area of heating for improving the water flow. A small chimney is associated with the pinnacle of the firebox for releasing the waste outlets at some larger height. The cleaning of the boiler can be done by the hand holes as well as manholes of the tubes & shell of the boiler.
These boilers include a water level indicator, a pressure gauge, steam stop tap security tap, & a manhole like mountings for providing security as well as the simplicity of working. The Fuel burns on the grate of the firebox in the boiler and the resultant hot-flue gases are permitted to flow in the region of the cross tubes.
The water nearby the cylindrical type firebox also gets heat through radiation as well as convection, therefore steam will be generated. The flow of water in the boiler will be based on the difference of density within water that is formed with the temperature difference.
Types of Fire Tube Boiler
The different types of this boiler include the following.
1) Cornish Fire Tube Boiler
The first Cornish boiler was approved by an engineer namely “Trevithick a Cornish”. This kind of boiler includes a plane cylindrical shell, as well as a tiny flue pipe holding the heating system, flows through it.
2) Lancashire Fire Tube Boiler
The construction of the Lancashire, the boiler is related to Cornish boiler but as a substitute of one flue pipe, two flue pipes are utilized.
3) Locomotive Fire Tube Boiler
The locomotive boiler is an inactive boiler that is used in train engines. This type of boiler is capable while producing steam as well as it is solid. The design of the locomotive boiler is horizontal multi tubular. The main advantage of using this type of boiler is low cost for construction, installation, and steam capacity is high.
Locomotive Fire Tube Boiler
4) Vertical Fire Tube Boiler
The vertical boiler is simple, and it comprises a cylindrical shell enclosed a larger section of water, and the rest of the section will be occupied with steam. It contains cross tubes and a furnace at the bottom of the boiler. The combustion gases after heating the water are allowed to escape into the atmosphere.
Vertical Fire Tube Boiler
5) Cochran Fire Tube Boiler
The Cochran boiler is a vertical type multi-tubular boiler, and it includes several horizontal fire tubes. The heating system is one part of the construction and it is perfect.
6) Scotch Marine Fire Tube Boiler
The Scotch marine boiler is a very popular boiler used for high vapor capacities at high forces. This type of boiler includes a huge number of tiny diameter tubes for providing the benefit of the high-heating region of the surface. The boilers are fired up internally and leave from the boiler using a chimney to the environment.
Scotch Marine Fire Tube Boiler
7) Immersion Fire Tube Boiler
The immersion type boiler is a single flow boiler that was expanded in the year 1940 by Sellers Engineering. It includes fire tube only, works as a boiler as well as the burning chamber. By several burners, needles inserting premixed air & normal gas below pressure. It maintains condensed thermal pressures and requires brick-work totally because of its construction.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of this boiler includes the following.
· Designing of this boiler is simple and less maintenance price.
· It applies to small-scale industries
· Fewer experts are enough for the operation
· No pure water is necessary
· Treatment of feed water is not very essential this boiler
The disadvantages of this boiler include the following.
· The efficiency of this boiler is up to 75%
· The variation of the load cannot
· It occupies more floor area
· The working pressure of this boiler is maximum of 20 bar
· The handling of load fluctuations is not easy.
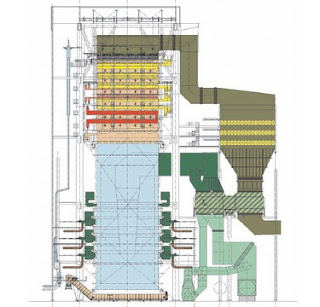
A high-pressure water tube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam pass through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater]] to become superheated. Superheated steam is defined as steam that is heated above the boiling point at a given pressure. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower drum via large-bore 'downcomer tubes', where it pre-heats the feedwater supply. (In large utility boilers, the feedwater is supplied to the steam drum and the downcomers supply water to the bottom of the waterfalls). To increase the economy of the boiler, exhaust gases are also used to pre-heat combustion air blown into the burners, and to warm the feed water supply in an "economizer". Such watertube boilers in thermal power stations are also called steam generating units.
Application -
· Variety of process applications in industries
· Chemical processing divisions
· Pulp and Paper manufacturing plants
· Refining units
Different Types of Fuels Used in Boilers
Whether it's a fire-tube boiler, tubeless boiler, hot water boiler, water-tube boiler, or any other classification, all systems will utilize one or more than one of the different boiler fuel types. In fact, many boiler models are actually distinguished and characterized by the different boiler fuel types it uses.
The type of fuel a boiler uses is critical for a range of reasons, but it plays a direct role in determining the operating costs as well as environmental impact. As a result, it’s vital to understand and be familiar with all of the different boiler fuel types. Let’s take a closer look at each of the different boiler fuel types:
- Natural gas
- Electricity
- Heating oil
- Solid fuels
- Renewable energy sources
- LPG
Natural Gas: As the most common type of residential boiler fuel, natural gas is relatively inexpensive and readily available. Yet, considering natural gas burns cleanly and is easy to transport, it is a wildly popular residual type of boiler fuel.
The key concern surrounding natural gas is it can be up to 90% methane gas, which is a dangerous greenhouse gas that can be 34% more potent than CO2. Although methane gas may be inert whenever it is burned, it causes significant damage to the ozone once it makes its way into the atmosphere. Even though natural gas is cheap, it comes with a hefty environmental impact.
Electricity: They are much better because of their many advantages over other fuel sources. They are noiseless, very light compared to another boiling vessel, and have a low operation and maintenance costs.
Heating Oil: Heating oil is a low viscosity, a liquid petrolium product used as a fuel oil for furnaces or boilers in buildings. Home heating oil is often abbreviated as HHO.
Heating oil consists of a mixture of petrolium derived hydrocarbons in the 14- to 20-carbon atom range that condenses between 250 and 350 °C (482 and 662 °F) during oil refining.
Solid Fuels: The fuel a solid fuel boiler runs on is referred to as “solid fuel”, solid fuel can take many forms, such as coal, wood, paper – the safe fuel you would normally feed a fire with at home, although it is highly advised against feeding a solid fuel boiler with processed types of household rubbish that are often used in fires or bonfires, due to the increased risk of mess, blockages or even combustion.
It has been argued that solid fuel systems are messy and inefficient due to their nature of being an open fire, and, being an open fire, they require a thorough cleaning out at least once a day to ensure it burns effectively.
Renewable Energy Sources: Biomass is an attractive renewable fuel in utility boilers. Biomass energy is a renewable energy source because it is produced from organic materials such as plants and manure. The most common forms used to generate biomass energy are wood, crops, and manure.
Biofuels are a form of renewable energy derived from burning plant or animal substances, otherwise called combustion. One of the challenges to biofuels has been that it is not easily transferred into a liquid form which is the primary method used to fuel most cars and homes.
LPG: LPG stands for Liquefied Petroleum Gas and it is a combination of gaseous hydrocarbons, produced from natural gas and oil extraction (66%) and from oil refining (34%). In addition to being used in domestic heating systems, LPG is also often used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and vehicles, as well as for refrigerants and aerosol propellants. It can be stored and transported in small canisters, large tanks, and lorries.
An LPG boiler works in a very similar way to both natural gas and oil boilers i.e. the boiler burns the fuel to produce the energy needed to heat water from the mains supply.
Industrial Application of boilers
Boilers have various cross-markets application in the industry.
The various applications of the industrial boilers are,
- Operating steam engines.
- Operating steam turbines.
- Operating reciprocating pumps.
- Industrial process work in chemical engineering.
- For producing hot water required to be supplied to room in very cold areas.
- In thermal power stations.
- The heat content of the steam is large and thus it is suitable for process heating in many industries like sugar mills, textile mills, dairy industry, and also chemical industries.
Boilers are used in Breweries for various purposes like
a.
The heating of large kettles where beer is brewed in batches.
b. Creating enough hot water for sanitization and sterilization.
c. The heat produced is used for pasteurization and etc.
They are also used in the Food Processing industry, for meat and poultry processing, Vegetable Processing, etc.
The major application of boilers is in the Power generation industry. In the power generation industry, Supercritical steam generators are used to produce electricity. They operate at supercritical pressure. In contrast to a subcritical boiler a supercritical steam generator operates at such a high pressure (over 3200 psi or 22 MPa) that the physical turbulence that characterizes boiling ceases to occur, the fluid is neither in the liquid state nor in a gas bit is a super critical fluid. There is no generation of steam bubbles within the water because the pressure is above the critical pressure point at which steam bubbles can form. As the fluid expands through the turbine stages, its thermodynamic state drops below the critical point as it does work turning the turbine which turns the electrical generator from which power is ultimately extracted. The fluid at that point may be a mix of steam and liquid droplets as it passes into the condenser. This results in slightly less fuel use and therefore less greenhouse gas production. The term "boiler" should not be used for a supercritical pressure steam generator, as no "boiling" occurs in this device.
References: https://www.stheatingservices.co.uk/types-fuel-used-boiler/
https://www.atiofny.com/boiler-fuel-types/











Such a systematic blog it is, proper use of diagrams for better explanation, theory. Each and every point is explained so well. Great work👏
ReplyDeleteVery thorough explanation👍👍
ReplyDelete